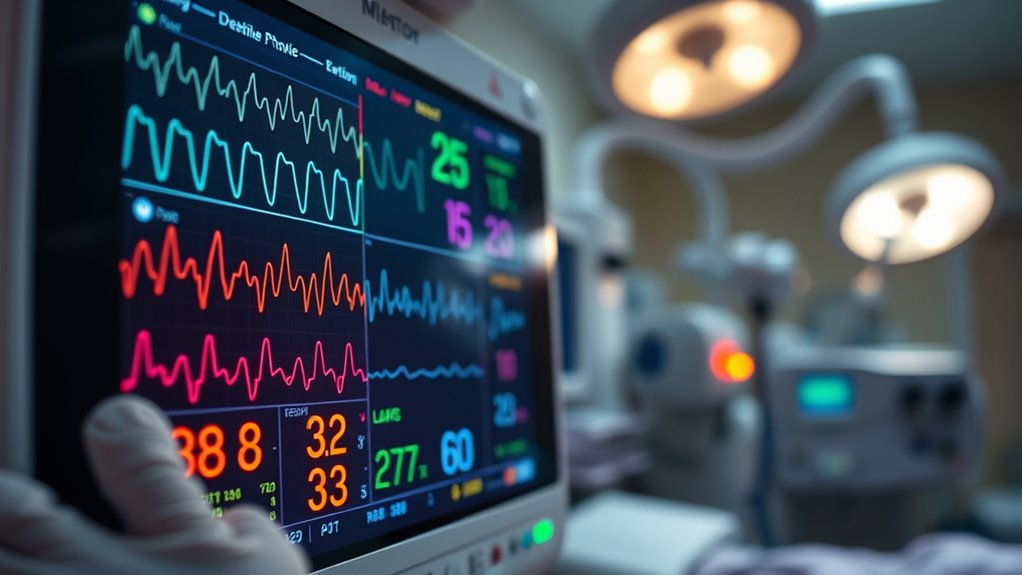
To read a hospital monitor effectively, focus on key essential signs. Heart rate is shown in beats per minute (BPM), with normal ranges between 60 and 100 BPM. Blood pressure displays two numbers: systolic (during beats) and diastolic (between beats). Oxygen saturation, measured in percentage, should ideally be 95% or higher. Finally, respiratory rate indicates breaths per minute. Understanding these metrics is important for evaluating patient health status. You’ll find more significant details on this topic ahead.
Understanding Vital Signs Monitors
When you approach a essential signs monitor, it’s important to understand its core functions, as these devices provide critical information about a patient’s health status. Key signs monitors come in various types, each tailored to track specific metrics such as heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation. Familiarizing yourself with these monitor types enhances your ability to interpret data accurately, which is fundamental for patient safety. You’ll notice that each reading can indicate changes in a patient’s condition, requiring prompt attention or intervention. Understanding how to read these monitors empowers you to act decisively, ensuring that patients receive the care they need. Ultimately, being informed about monitor functions contributes considerably to enhancing overall patient safety within healthcare settings.
Heart Rate: What the Numbers Indicate
Understanding heart rate is essential, as it serves as an important indicator of a patient’s cardiovascular health. The heart rate, measured in beats per minute (BPM), varies within specific heart rate zones that reflect different levels of exertion and fitness. For instance, resting heart rates typically range from 60 to 100 BPM. Lower rates may indicate better cardiovascular fitness, while higher rates could signal stress or medical issues. Additionally, heart rate variability (HRV) measures the time interval between heartbeats, providing insights into autonomic nervous system function. A higher HRV generally indicates better health and resilience, while lower HRV can suggest stress or potential health concerns. Monitoring these metrics helps you understand overall cardiovascular condition and guide recovery strategies.
Blood Pressure Readings Explained
Heart rate isn’t the only vital sign that provides insight into a patient’s health; blood pressure readings are equally important. Blood pressure measures the force of blood against artery walls, reported as two numbers: systolic (pressure during heartbeats) and diastolic (pressure between beats). Understanding these readings helps you gauge cardiovascular health. Measurement techniques can vary, including manual cuff methods and automated devices, each offering accuracy when used correctly. High blood pressure may indicate stress on the heart, while low readings could suggest inadequate blood flow. Regular monitoring is essential, as fluctuations can signal underlying issues. By comprehending these values, you empower yourself to participate in health discussions with your healthcare team, enhancing your ability to advocate for your well-being.
Oxygen Saturation and Its Importance
Oxygen saturation is a critical indicator of how well your body is delivering oxygen to its tissues. Measured through pulse oximetry, this value reflects the percentage of hemoglobin in your blood that is saturated with oxygen. Normal oxygen levels typically range from 95% to 100%. When levels drop below this threshold, it can signal inadequate oxygenation, which may lead to serious health issues. Monitoring your oxygen saturation can help identify respiratory problems early, allowing for timely intervention. If you’re in a hospital setting, keeping an eye on these readings can empower you to participate actively in your care. Understanding your oxygen saturation is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being.
Respiratory Rate: How to Interpret It
Respiratory rate, measured as breaths per minute, is an essential sign that provides insight into your respiratory function and overall health. Monitoring your respiratory patterns helps identify any abnormalities, as changes in rate can indicate underlying issues. A normal respiratory rate for adults typically ranges from 12 to 20 breaths per minute. Understanding the rate significance can empower you to recognize potential health concerns early.
| Respiratory Rate (bpm) | Pattern | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| 12-20 | Normal | Healthy respiratory function |
| 20-30 | Tachypnea | Possible respiratory distress |
| 10-12 | Bradypnea | Potential respiratory depression |
| Below 10 | Severe Bradypnea | Critical condition requiring attention |
Cardiac Monitors: Deciphering the Waveforms
Monitoring essential signs like respiratory rate can provide critical clues about a patient’s health, but understanding cardiac monitors is equally important. Cardiac monitors display ECG waveforms that reflect the heart’s electrical activity. You’ll notice distinct shapes like the P wave, QRS complex, and T wave, each representing different phases of the cardiac cycle. Recognizing these waveforms helps you identify normal patterns and detect arrhythmia patterns, which can signify underlying issues. For example, a prolonged QRS may indicate a bundle branch block, while irregular rhythms could signal atrial fibrillation or other arrhythmias. Familiarizing yourself with these waveforms enhances your ability to respond to potential cardiac events effectively, ultimately supporting patient care and safety.
Engaging in Patient Care: Questions to Ask
Understanding a patient’s needs requires more than just observing essential signs; it involves asking the right questions to gather detailed information about their condition. Effective patient communication fosters caregiver collaboration, ensuring thorough care. Here are some significant questions you might consider:
| Question | Purpose | Follow-up |
|---|---|---|
| How are you feeling today? | Assess current symptoms | Can you describe any pain? |
| Have you noticed any changes? | Understand condition evolution | When did this start? |
| What concerns do you have? | Address worries | What would you like to know? |
Frequently Asked Questions
What Should I Do if the Monitor Beeps Continuously?
When the monitor alarms continuously, don’t panic. Check the patient’s response first. Is there a change in their condition? If unsure, alert the medical staff immediately for assessment and intervention. Your vigilance matters.
Can I Change the Settings on the Monitor?
No, you shouldn’t change the monitor settings without proper authorization. Adjustments can compromise patient safety. Always consult with a healthcare professional to guarantee the monitor functions correctly and maintains accurate readings for ideal care.
How Often Are Vital Signs Recorded?
Essential signs frequency typically ranges from every 15 minutes to every hour, depending on monitoring protocols. You’ll find these intervals important for evaluating patient stability, ensuring timely interventions and maintaining ideal care standards.
What Is the Normal Range for Each Vital Sign?
Normal essential signs include a heart rate of 60-100 bpm, blood pressure around 120/80 mmHg, respiratory rate of 12-20 breaths per minute, and a temperature between 97°F and 99°F. Essential sign ranges vary slightly among individuals.
Why Are There Different Monitors for Different Patients?
Different monitors cater to varying patient needs, with studies showing that 70% of critical patients benefit from specialized monitoring. Each monitor type is designed to track specific essential signs critical for tailored treatment and patient safety.