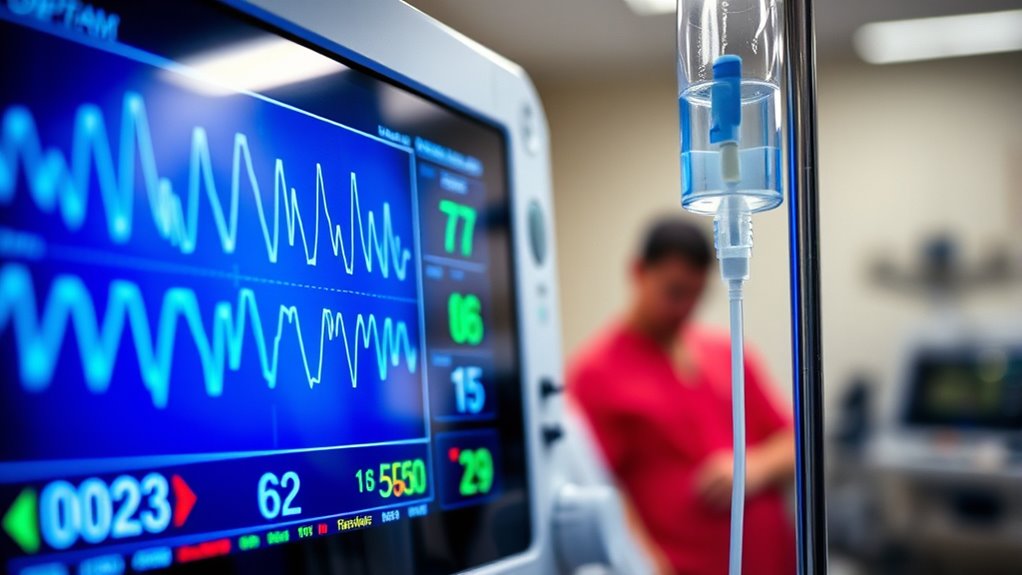
To effectively read a hospital monitor, you need to understand the crucial signs displayed: heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation. Heart rate should range from 60 to 100 beats per minute, while blood pressure readings indicate categories from normal to hypertension. Oxygen saturation levels should ideally be between 95% to 100%. Recognizing alarms is essential, as they signal critical changes. Mastering these elements will enhance patient assessment and response. More insights await as you explore further.
Understanding Vital Signs: The Basics
Significant signs are essential indicators of a patient’s health status, providing critical information about their physiological condition. A key signs overview typically includes measurements such as temperature, blood pressure, respiratory rate, and oxygen saturation. These elements serve as fundamental monitor components, allowing healthcare professionals to assess and respond to a patient’s needs effectively.
Understanding these signs is important for anyone seeking to maintain their health or that of others. They can reveal underlying issues before they escalate, empowering you to make informed decisions. Regularly monitoring key signs can help identify trends, ensuring timely interventions when necessary. By grasping these basics, you can better advocate for your health and navigate the complexities of medical environments with confidence.
Heart Rate: What It Tells You
Heart rate is one of the most significant essential signs monitored in a hospital setting, providing immediate insight into a patient’s cardiovascular health. It reflects how well your heart is functioning, with normal ranges typically between 60 and 100 beats per minute for adults. Monitoring heart rate variability is vital, as it indicates the autonomic nervous system’s responsiveness. A higher variability often suggests better cardiovascular fitness and stress resilience, while lower variability can signal potential health issues. Abnormal heart rates, whether too fast or too slow, may require further investigation. By understanding heart rate and its implications, you can better appreciate the information your monitor provides, guiding healthcare decisions and interventions.
Blood Pressure: Interpreting the Readings
While monitoring blood pressure may seem straightforward, understanding its readings is essential for evaluating a patient’s overall cardiovascular health. Blood pressure is categorized into several ranges: normal, elevated, and various stages of hypertension. Normal readings are typically below 120/80 mmHg, while elevated blood pressure falls between 120-129/80 mmHg. Stage 1 hypertension ranges from 130-139/80-89 mmHg, and Stage 2 hypertension is 140/90 mmHg or higher. Recognizing these categories helps in hypertension management, guiding treatment decisions. If you see consistent high readings, it’s vital to monitor lifestyle factors and consider medical interventions. Clear comprehension of these readings empowers you to take proactive steps in maintaining cardiovascular well-being and addressing potential health risks effectively.
Oxygen Saturation: The Importance of SpO2
Oxygen saturation, often measured as SpO2, is an essential indicator of a patient’s respiratory function and overall oxygen delivery to tissues. Monitoring SpO2 levels can help you assess the effectiveness of oxygen therapy. A pulse oximeter, a non-invasive device, provides real-time readings of oxygen saturation, allowing healthcare providers to make informed decisions about treatment. Generally, a healthy SpO2 level ranges from 95% to 100%. Levels below this range may indicate hypoxemia, a condition requiring immediate attention. Understanding these readings empowers you to engage in your care actively, ensuring you’re receiving the appropriate interventions. Regular monitoring of SpO2 can be critical for those with chronic respiratory conditions, allowing for timely adjustments to oxygen therapy when necessary.
Recognizing Alarms: What to Look For
Understanding the types of alarms on a hospital monitor is essential for effective patient care. You’ll need to recognize alarm prioritization levels to determine the urgency of each signal and follow established response protocols accordingly. This knowledge guarantees timely and appropriate actions in critical situations.
Types of Alarms
As you monitor a patient’s crucial signs, recognizing the types of alarms can be essential for timely interventions. Alarm types generally fall into three categories: physiological, technical, and system alerts. Physiological alarms indicate changes in critical signs, such as heart rate or blood pressure, triggering immediate attention. Technical alarms signal equipment malfunctions, like lead disconnections or low battery status, which require prompt troubleshooting. System alerts provide updates on monitoring software or connectivity issues, ensuring your equipment functions effectively. Understanding these alarm functions helps you prioritize actions efficiently, ultimately enhancing patient care. Always be attentive to these alarms, as they serve as crucial communication tools in a hospital setting.
Alarm Prioritization Levels
While monitoring a patient, it is crucial to recognize the prioritization levels of alarms, which can greatly impact your response time and decision-making. Alarms are categorized by alarm types, such as critical, warning, and advisory, each reflecting different levels of response urgency. Critical alarms typically indicate life-threatening situations requiring immediate intervention, while warning alarms signal potential issues that should be addressed promptly. Advisory alarms often pertain to non-critical alerts that warrant attention but can be addressed after more urgent matters. Understanding these levels helps you prioritize effectively, ensuring that you respond to the most critical situations first. By mastering alarm prioritization, you enhance patient safety and improve overall care delivery in the hospital setting.
Response Protocols Explained
When alarms sound, it’s essential to quickly identify their significance and act accordingly. Familiarize yourself with response protocols to guarantee patient safety. Each alarm indicates specific conditions; some require immediate actions, while others may signal routine checks. For example, a rapid heart rate might necessitate urgent intervention, whereas a low battery alert may simply require you to replace the power source. Always assess the patient’s condition in conjunction with the alarm. If unsure, consult with a healthcare professional to confirm the appropriate course of action. Remember, timely recognition and response can be lifesaving, so always stay alert and informed about the monitoring equipment and its implications for patient care. Your readiness is key in a dynamic hospital environment.
Practical Tips for Quick Assessments
To conduct quick assessments while monitoring patients, it’s essential to grasp the readings displayed on the monitor. You should also recognize alarm signals promptly and understand their significance. Prioritizing these elements will enhance your ability to respond effectively to patient needs.
Understand Monitor Readings
Understanding monitor readings in a hospital setting is essential for timely and effective patient care. Familiarize yourself with various monitor types, such as cardiac monitors, pulse oximeters, and blood pressure devices. Each type presents unique data that requires distinct reading techniques. Start by identifying the primary parameters displayed—heart rate, oxygen saturation, and blood pressure, for example.
Use a systematic approach: quickly glance at the trends, then focus on absolute values. Take note of any abnormalities and correlate them with the patient’s clinical picture. Remember that consistent practice enhances your reading skills and boosts your confidence. By mastering these techniques, you’ll be able to assess patient conditions swiftly and accurately, ensuring ideal care in critical situations.
Recognize Alarm Signals
Recognizing alarm signals is a crucial skill in monitoring patient safety. Quick assessments can mean the difference between life and death, so you need to be vigilant. Each alarm has its own significance, and understanding these can empower you to act swiftly.
| Alarm Type | Alarm Significance | Action Required |
|---|---|---|
| Heart Rate Alarm | Indicates potential arrhythmia | Check the patient’s pulse |
| Respiratory Alarm | Suggests breathing issues | Assess airway and breathing |
| Blood Pressure Alarm | Signals hypotension/hypertension | Evaluate vitals promptly |
Stay attentive to these signals to guarantee patient safety. Your ability to recognize and respond to alarms effectively can provide the freedom for patients to recover successfully.
Prioritize Patient Assessment
While it may seem overwhelming at times, prioritizing patient assessment is essential for effective monitoring and swift intervention. Start by reviewing the patient history; it provides critical insights into their condition and helps you identify potential complications. Utilize assessment techniques such as focused physical exams and targeted questions to quickly gather relevant information. Pay attention to key signs, as they can signal significant changes in status. Don’t forget to observe any changes in the patient’s behavior or responsiveness, as these can indicate the need for immediate action. By honing your assessment skills and utilizing available tools efficiently, you’ll guarantee that you’re prepared to act swiftly, ultimately prioritizing patient safety and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Often Should I Check the Monitor Readings?
You should check the monitor readings at regular intervals, ideally every 1-2 hours, depending on the patient’s condition. This monitor frequency guarantees you’re alerted to any changes that could require immediate intervention.
What Should I Do if Alarms Go Off?
When alarms go off, think of them as a lighthouse warning you of potential danger. Prioritize patient safety by promptly evaluating the situation, notifying the healthcare team, and following established alarm response protocols for effective management.
Can I Use a Monitor for Home Care?
Yes, you can use a monitor for home care. Various monitor types, like pulse oximeters and blood pressure monitors, allow you to track essential signs conveniently, enhancing your health management and independence in a home setting.
What if the Monitor Shows Inconsistent Readings?
If the monitor shows inconsistent readings, you should check its calibration and guarantee proper connection. Accurate reading interpretation is essential; consult a healthcare professional for guidance to confirm reliable monitoring and patient safety.
Are There Different Monitor Types for Different Patients?
Yes, there’re different patient monitor types tailored to individual needs. Specialized equipment, like cardiac monitors for heart patients or pulse oximeters for respiratory issues, guarantees accurate monitoring, enhancing patient care and promoting ideal outcomes.